はじめに
この記事ではmatplotlibのplt.barを使って棒グラフの棒をグラデーションカラーで表示する方法について解説します。単色ではなくグラデーションを適用することで、データの視覚的な魅力を高める手法を紹介します。
コード
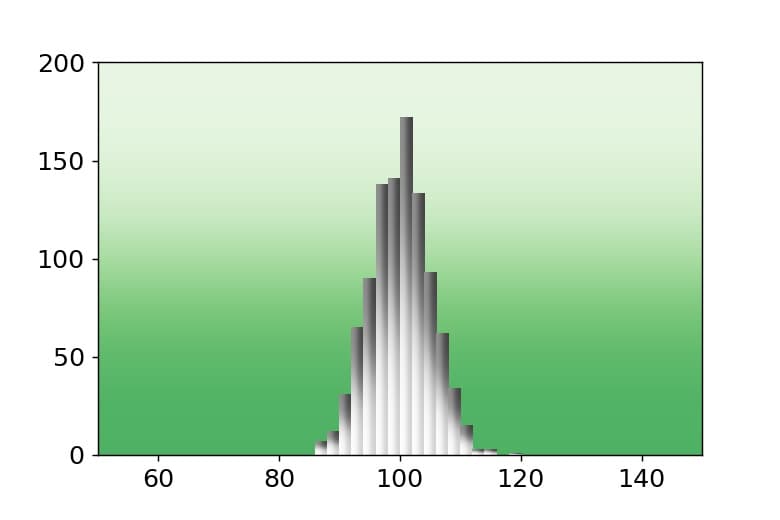
解説
モジュールのインポートなど
グラデーションカラー生成関数
axパラメータでは、グラデーションカラーを表示する図を指定します。 extentは図中の表示範囲を設定します。デフォルトではデータ座標が使用されるため、相対的な座標で設定するには「transform=ax.transAxes」のように指定します。
directionパラメータはグラデーションの方向を制御し、0で垂直方向、1で水平方向になります。
cmap_rangeではカラーマップの範囲を指定します。最小値は0、最大値は1です。
phiで角度を指定し、単位ベクトルvでグラデーションの方向を定義します。Xで4隅の座標を取得し、a,bの大きさに合わせたXを最終的に得ます。これをimshowで表示する際に「interpolation=’gaussian’」を設定することでグラデーションカラーが生成されます。
以下では、directionの値を変更した場合の表示の変化を示します。
#direction = 0.5
#direction = 1
#direction = 0
#direction = 0, a,b =.8,.2
a, bを降順にすることでグラデーションを逆にすることができます。
グラデーション棒グラフ生成関数
棒グラフの角棒のleft, right, bottom, topを取得して、gradient_imageを適用します。
軸範囲の設定
図の生成
背景の設定
extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), transform=ax.transAxesとすることで図全体にグラデーションカラーを表示できます。
データの生成
norm.rvsで正規分布に従うランダムデータを生成します。
棒グラフの表示
gradient_barでグラデーションカラー棒グラフを表示できます。
まとめ
matplotlibを使って棒グラフにグラデーションカラーを適用する方法を紹介しました。この手法を活用することで、データの視覚的表現が向上し、より魅力的なグラフを作成できます。カラーマップのカスタマイズによって、様々な表現が可能になります。
コメント
[…] [matplotlib] 58. 棒グラフのbarをグラデーションカラーで表示matplotlibのplt.barで表示する棒グラフの棒の色をグラデーションカラーで表示する方法について説明する。sabopy.com2020.01.29 […]