はじめに
本記事では、Python lmfitライブラリを使用した重み付き最小二乗法によるガウシアンフィッティングの手法を解説します。実践的なコード例を交えながら、一連のプロセスを詳細に説明していきます。
コード
解説
モジュールのインポート
バージョン
データの生成
rng = default_rng()を設定し、rng.normal(0,1,10000)を使って標準正規分布に従うランダムデータ10000個を生成します。xとyの関係を図示すると以下のようになります。
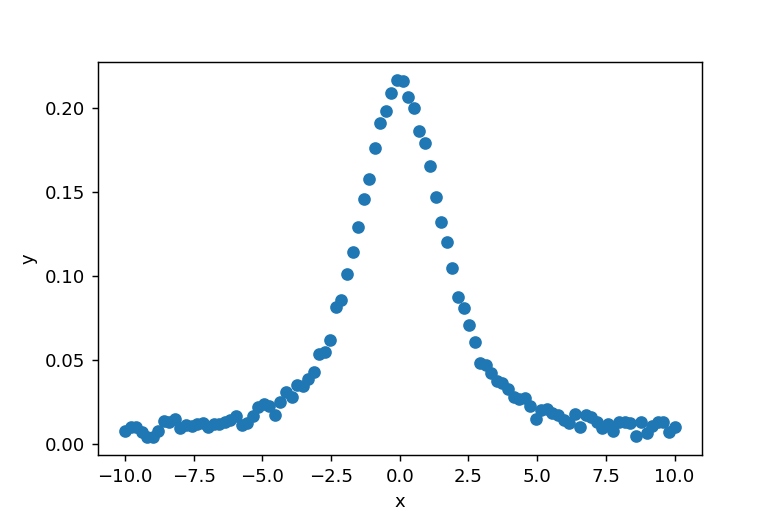
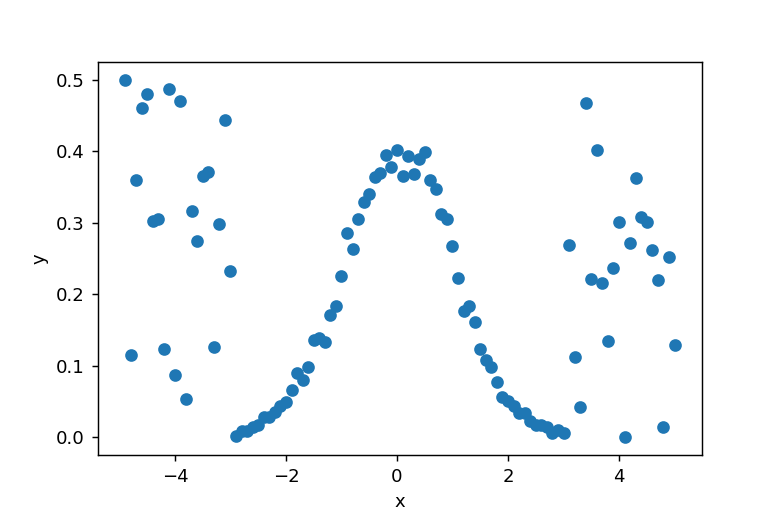
y値の両端20個にランダムなデータを付加します。xとyの関係を図で示すと以下のようになります。

モデルの定義
lmfit.models モジュールのGaussianModel をモデル関数として使用します。Gaussian関数は以下の式で表され、パラメータは振幅(amplitude)、中心(center)、標準偏差(sigma)の3つです。
\[f(x; A, \mu, \sigma) = \frac{A}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{[{-{(x-\mu)^2}/{{2\sigma}^2}}]}\]
初期パタメータの推定
model.guess(y, x=x)を使用して、上図のデータをガウス関数モデルで近似するためのフィッティングパラメータの初期値を推定します。得られるパラメータ(params)は以下のようになります。
カーブフィット
model.fit(y, params, x=x)により、カーブフィッティングを実行します。
フィッティング結果の表示
print(result.fit_report())により、フィッティングの結果を見ることができます。
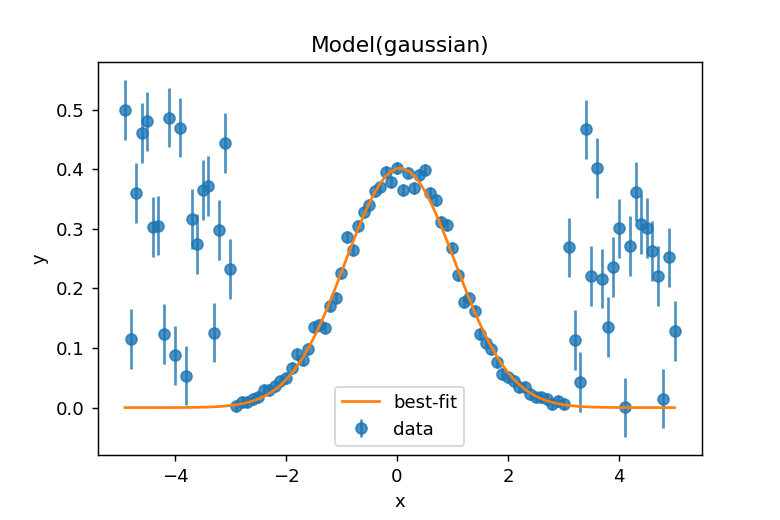
result.plot_fit()によりデータとフィッティングカーブが表示されます。
両端のデータに引っ張られて、適切なフィッティングができていないことが明らかです。この問題を解決するために、重み付き最小二乗法によるフィッティングを実施します。
重み配列の作成
重み配列を作成します。データの両端に異常値がある部分は重みを小さく設定します。この重み配列はデータと同じ形状である必要があります。
重みを利用したカーブフィット
model.fit()メソッドにweightsパラメータを指定することで、重み付き最小二乗法によるフィッティングが実行できます。
重みつきカーブフィットの結果の表示
result.plot_fit()を実行して結果を表示すると、以下のようなグラフが得られます。重み付けが適切に反映され、異常値の影響を受けない正確なフィッティング結果が確認できます。

コメント